Welcome to the official website of Laizhou Huayin Test Instrument Co., Ltd!
FAQ
What is hardness?How to classify hardness testers?Have the majority of hardness tester customers and companies in Shandong encountered the same problem?In technical terms, hardness refers to the ability of a material to resist hard objects pressing into its surface.Hardness is one of the important indicators to measure the performance of metal materials.Generally speaking, the higher the hardness, the better the wear resistance.Commonly used hardness indicators are Richter hardness, Brinell hardness, Rockwell hardness and Vickers hardness and so on.What are the categories of hardness testers?
1. Brinell hardness: A hardened steel ball of a certain size (diameter is generally 10mm) is pressed into the surface of the material with a certain load (generally 3000kg) and maintained for a period of time. After removing the load, the ratio of the load to its indentation area is calculated, which is the Brinell hardness value (HB). The commonly used unit is kilogram force/mm2 (N/mm2).(Brinell hardness tester)
2. Rockwell hardness: When HB>450 or the sample of the workpiece under test is too small, a Brinell hardness tester cannot be used to measure it. A Rockwell hardness tester should be used. It uses a diamond cone with an apex angle of 120° or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 and 3.18mm. Under a certain load, it is pressed into the surface of the material under test, and the hardness of the material is calculated from the depth of the indentation.According to the different hardness of the test material, it is expressed in three different scales: HRA: It is the hardness obtained by using a 60kg load and a diamond cone press, and it is used for materials with extremely high hardness (such as cemented carbide, etc.). HRB: It is a steel ball hardened with a load of 100kg and a diameter of 1.58mm. The calculated hardness is used for materials with lower hardness (such as annealed steel, cast iron, etc.). HRC: It is the hardness calculated using a 150kg load and a diamond cone press. It is used for materials with high hardness (such as quenched steel, etc.).(Huayin Rockwell Hardness Tester)
3. Vickers hardness: A diamond square cone press with a load within 120kg and an apex angle of 136° is pressed into the surface of the material, and the surface area of the indentation pit of the material is divided by the load value, which is the Vickers hardness HV value (kgf/mm2) 4 Richter hardness. The impact body of the specified quality is used to impact the surface of the sample at a certain speed under the action of elastic force. The value calculated by the ratio of the rebound speed and the impact speed of the punch at a distance of 1mm from the surface of the sample is named after Dr. LEEB, so it is called the Richter hardness conversion formula: 1.Shore hardness (HS) = Bo hardness (BHN)/10+12 2 .Shore hardness (HS) = Rockwell hardness (HRC) +15 3.Bo hardness (BHN) = Rock hardness (HV) 4.Rockwell hardness (HRC) = Bo hardness (BHN)/10-3.(Vickers hardness tester manufacturer)
Lubrication of the hardness tester: During the use of the hardness tester, regularly inject an appropriate amount of oil into the contact surface of the screw and the handwheel.
Cleaning of the hardness tester: Apply a dust cover to cover the machine, if the hardness tester is not in use for a long time.
Both are standards for testing hardness, the difference is that the measurement methods are different.
Brinell hardness (Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
Use a steel ball or cemented carbide ball of a certain diameter to press into the surface of the sample with a specified test force (F), remove the test force after a specified holding time, and measure the diameter of the indentation on the surface of the sample (L).The Brinell hardness value is the quotient obtained by dividing the test force by the spherical surface area of the indentation.Expressed in HBS (steel ball), the unit is N/mm2 (MPa).
The calculation formula is: F/π(d/2)2
Where: F-the test force pressed into the surface of the metal sample, N;
D--Diameter of steel ball for test, mm;
d--The average diameter of the indentation, mm.
The determination of Brinell hardness is more accurate and reliable, but generally HBS is only suitable for metal materials below 450N/mm2 (MPa), not for harder steels or thinner plates.Among the steel pipe standards, Brinell hardness is the most widely used, and the hardness of the material is often expressed by the indentation diameter d, which is both intuitive and convenient.The Brinell hardness test can also be used for non-ferrous metals and soft steels. Small sizes and thinner materials can be measured with small-diameter ball pressure heads.Brinell hardness testers are mostly used for the inspection of raw materials and semi-finished products. Due to the large indentation marks, they are generally not used for the inspection of finished products.
For example: 120HBS10/1000/30: It means that the Brinell hardness value measured by using a 10mm diameter steel ball under the action of 1000Kgf (9.807KN) test force for 30s (seconds) is 120N/mm2 (MPa).
Press a hardened steel ball of a certain size (generally 10mm in diameter) into the surface of the material with a certain load (generally 3000kg) and keep it for a period of time. After it is unloaded, the ratio of the load to its indentation area is the Brinell hardness value (HB), in kilograms of force/mm2 (N/mm2).
Rockwell hardness (which Brinell hardness tester is good)
Use a certain size of load P to press the quenched steel ball with a diameter of D into the surface of the metal material under test, hold it for a period of time and remove the load.The ratio of the load P to the indentation surface area F is the Brinell hardness value, which is denoted as HB.(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
Chinese name Brinell Hardness Foreign name Brinell Hardness Applied subject Physics application range 8~650HBW
Brinell hardness (HB) is generally used when materials are softer, such as non-ferrous metals, steel before heat treatment or after annealing.
Brinell hardness (HB) is a test load of a certain size. A hardened steel ball or cemented carbide ball of a certain diameter is pressed into the surface of the metal under test, maintained for a specified time, and then unloaded to measure the diameter of the indentation on the surface under test.
The Brinell hardness value is the quotient of the load divided by the spherical surface area of the indentation.Generally:
A certain size of hardened steel ball is pressed into the surface of the material with a certain load and maintained for a period of time. After the load is removed, the ratio of the load to its indentation area is the Brinell hardness value (HB), in kilograms of force/ (N/).(Rockwell hardness tester)
The test load and the diameter of the test steel ball need to be determined according to the actual performance of the material.(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
Brinell hardness, indentation spacing
In the Brinell hardness test, there should be a certain distance between the indentation and the indentation from the edge of the sample. If the indentation distance is too close, the deformation hardening zone generated around the first indentation will hinder the deformation of the indentation generated by the subsequent test.At the same time, the expansion of the deformation of the second indentation will also cause the first indentation to change in the direction of diameter.The distance between the center of the indentation and the edge of the sample should not be too small. If it is too small, significant plastic deformation will occur at the edge of the sample and cause deformity of the indentation. However, considering that the maximum diameter of the Brinell indentation ball is 10 mm, it is impractical to specify an excessive indentation spacing for samples with a smaller area. Therefore, the standard must determine a reasonable indentation spacing. Experimental observations show that under normal circumstances, the width of the hardened area around the indentation does not exceed half of the diameter of the indentation.After the revision of the standard, this provision has been revised.
In GB/T 231-84, the distance between the indentation marks and the distance between the indentation marks and the edge of the sample is specified as the distance between the center of the indentation and the edge of the sample should not be less than 2. The average diameter of the indentation. 5 times.The distance between the centers of two adjacent indentation marks should not be less than at least 4 times the average diameter of the indentation.When the Brinell hardness is less than 35, the above distance should be 3 times and 6 times the average diameter of the indentation, respectively.”(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
After the revision of the new standard, the changes are as follows:
“The distance between the center of any indentation and the edge of the sample is at least 2.5 times the average diameter of the indentation. 5 times.The distance between the centers of the two adjacent indentations is at least 3 times the average diameter of the indentation.”
The reason for the modification is equivalent to ISO 6506-1, and the test results show that these modifications have no effect on the test results.(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
Among the methods of measuring hardness by static force, the Vickers hardness test method is the most accurate one. This method has a wide range of hardness measurement and can determine the hardness of most metal materials currently used.When the structure of the test material is relatively uniform, the Vickers hardness test results obtained by different test forces are similar.The indentation of Vickers hardness is square, with a clear outline, and the hardness value calculated by measuring the diagonal length is highly accurate and repeatable.(Huayin Hardness Tester)
According to the scope of the test force, this method can be subdivided into Vickers hardness test, small load Vickers hardness test and microscopic Vickers hardness test methods.Can be based on the size of the test area.Three methods are used for the thickness of the sample and the hardness of the sample.For the determination of the hardness of thin surface layers such as carburizing layer and nitriding layer, as well as the determination of the hardness of very thin materials, the test can be carried out under very small test force conditions (Rockwell hardness tester manufacturer)
On the basis of merging the original three standards, the new standard adjusts the applicable diagonal length range of indentation.(Brinell hardness tester)
Leeb hardness test: the hardness is calculated by the ratio of punch rebound velocity to impact velocity, and the corresponding symbols are used for different impact devices Table 7K.
Comparison of traditional Brinell and bathymetric Brinell hardness testing
1. Advantages and disadvantages of traditional Brinell hardness testing (Laizhou Huayin hardness tester)
The traditional Brinell measurement method uses a cemented carbide ball of a certain diameter to press into the surface of the sample under the action of a specified test force F. After a certain test force is maintained for a certain time, the test force is removed, and the diameter d of the indentation left on the surface of the sample is measured. The Brinell hardness is calculated by dividing the test force by the quotient of the indentation surface area S.The advantages of this method are: the indentation is large, the hardness value is slightly affected by the microscopic segregation of the sample tissue and the uneven composition, the dispersion of the test results is small, the reproducibility is good, and the tensile strength value of the material has a good correspondence, so it can more objectively reflect the true mechanical properties of the material.Due to the above-mentioned advantages of the Brinell hardness test method, it has been widely used in the industrial field and is used to detect castings, forgings, steel, tempering and annealing, normalizing parts, and non-ferrous metals. It has become one of the most widely used and commonly used hardness testing methods.Traditional Brinell hardness measurement has the following disadvantages:
1.There are more steps when testing the sample, and the detection time is longer
The Brinell hardness testing method is obtained by indentation on the surface of the sample. When performing Brinell hardness testing, a certain experimental force and an indenter of a certain diameter must first be selected to apply force to the sample, and then the diameter of the indentation is measured with a special reading microscope, and finally the Brinell hardness value is obtained according to the measured indentation diameter look-up table. The whole step is cumbersome and time-consuming.
2.Easy to introduce human error (Laizhou Huayin hardness tester)
Traditional Brinell hardness testing adopts a manual method and uses a reading microscope to read the indentation, so that the diameter of the indentation will be biased due to various human factors.
3.High labor intensity
The diameter of Brinell hardness indentation is generally only about 4mm, and measuring hundreds of indentation marks a day will make people feel dazzled and tired.;
4.Cannot be tested on curved surfaces
According to the principle of Brinell hardness testing, Brinell hardness testing can only be tested on a plane. For curved samples, a small plane must be polished by mechanical or manual methods before Brinell hardness testing can be carried out.
Hardness is one of the commonly used indicators for evaluating the mechanical properties of metal materials. As far as the standardized metal hardness test methods are concerned, the essence of hardness is the ability of the material to resist the pressure of another harder material.At present, our country already has national standards for metal Brinell hardness, Vickers hardness, Rockwell hardness, Richter hardness, Knoop hardness and Shore hardness test methods. Due to the different principles of each hardness test method, “hardness” itself is an uncertain physical quantity, that is, for the same sample, the hardness values measured by different methods are completely different, and the various hardnesses reflect the comprehensive properties of various physical properties such as material elasticity, plasticity, strength, toughness and wear resistance under the test conditions specified by each other.(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
In the past, for a long period of time, my country did not have its own hardness and strength conversion table, but only quoted foreign conversion tables.However, in use, due to factors such as the chemical composition of the material, the processing technology, the geometry of the sample, and the accuracy of the measuring instruments in various countries, the basis for the establishment of the conversion relationship between hardness and strength, and the different data processing methods, it is found that there are large differences between the various conversion values.In addition, since there is no unified domestic standard, different conversion tables are used, which can easily cause confusion in the conversion values of hardness and strength.In view of this, since 1965, the Chinese Institute of Metrology and other units have established Brinell, Rockwell, Vickers and surface Rockwell hardness benchmarks and force value benchmarks. Through a large number of tests and analytical studies, the correspondence between the various hardness and strength of ferrous metals has been discussed. After production verification, our country has formulated its own "Ferrous Metal Hardness and Strength Conversion Table" suitable for 9 steel systems and regardless of steel type.In the verification work, more than 100 units participated, and a total of more than 3,000 samples were processed and more than 30,000 data were measured.The verification data is relatively evenly distributed on both sides of the conversion curve, and the results are basically in line with the normal distribution, that is, these conversion tables are basically in line with the actual situation and are available.(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
These conversion tables have been internationally compared with similar conversion tables in 10 countries, and the conversion values of our country are roughly the average of the conversion values of various countries.
The "Ferrous Metal Hardness and Strength Conversion Table“ was adopted by the National Technical Appraisal Conference in December 1973. The original standard number was ”GB 1172-74“, and then confirmed in 1999. The current standard number is ”GB 1172-99".(Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
In February 1975, the National Bureau of Standards and Metrology organized the Chinese Academy of Metrology to form a research group with relevant subordinate units such as the former Ministry of Aerospace Industry, the Ministry of Aviation Industry, the Ministry of Metallurgical Industry, and the Ministry of Electronics Industry. There are also 18 scientific research and production units to undertake collaborative tasks.After several years of hard work, on the basis of domestic materials, 20 sets of conversion formulas formed based on nearly 80,000 test and verification data, 9 conversion scales are listed, and our country's own “Aluminum alloy hardness and strength conversion” standard has been established. The standard was approved at the April 1982 review meeting and promulgated in 1983.The conversion table includes the conversion of the hardness and strength of brass (H 62, HPb59—1), the various hardness and tensile strength (σb), yield strength (σ0.2) and elastic limit (σ0.01) of beryllium bronze (QBe 2), etc. The conversion table includes the conversion of the hardness and strength of brass (H 62, HPb59-1), and the conversion of the various hardness and tensile strength (σb) of beryllium bronze (QBe 2).Its national standard number is GB 3771-83.
Introduction to Brinell hardness testing method
The Brinell hardness testing method is developed by Swedish engineer J.A.Brinell proposed it from 1899 to 1900 when studying the effects of heat treatment on the organization of rolled steel.This hardness testing method is the earliest hardness testing method used. The reason why it is still widely used today is because the indentation obtained by the Brinell hardness testing method is large and its hardness value is less affected by the uneven composition of the sample under test. The dispersion of the test results is small, and the reproducibility is good, which can well reflect the true hardness value of the material.
1. Brinell hardness testing principle and calculation formula (Laizhou Huayin hardness Tester)
Use a cemented carbide ball of a certain diameter to press into the surface of the sample under the action of a specified test force F. After a certain test force is maintained for a certain time, the test force is removed, and the diameter of the indentation left on the surface of the sample is measured. d, Brinell hardness is calculated by dividing the test force by the quotient of the indentation surface area S.The calculation formula is as follows:
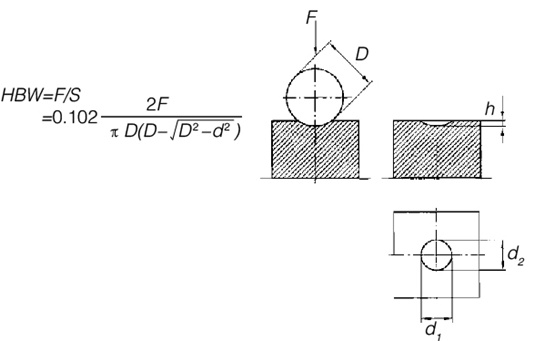
2. The scope of application of Brinell hardness testing method (Laizhou Huayin hardness tester)
The pressure and the diameter of the indenter used in Brinell hardness testing are large, and the diameter of the indentation obtained is also large. This determines that this hardness testing method is suitable for detecting metal materials with large grains, such as castings, forgings, steels, tempering and annealing, normalizing parts, and non-ferrous metals and their alloys.Especially for some soft metals, it has very accurate detection properties, such as aluminum, copper, lead, tin, zinc and their alloys.
The Brinell hardness testing method also has its limitations in practical applications. This testing method first requires a certain test force to be applied to the sample under test, and then a special optical instrument is used to read the indentation, and finally the Brinell hardness value can be obtained by looking up the table.The inspection process takes a long time to operate and has many steps. In addition, due to the relatively large selection of test force and indenter diameter, the indentation marks obtained are generally large, which is a lossy detection method.
3. Precautions when using Brinell hardness testing method (Laizhou Huayin Hardness Tester)
1. The Brinell hardness value of workpieces tested in industrial production should be strictly implemented in accordance with relevant national standards.
2. Under normal circumstances, the ambient temperature during testing should be between 10 and 35℃.
3. In the Brinell hardness testing, please select the test force and the diameter of the indenter according to the relevant provisions of the national standard for the selection of the test force and the diameter of the indenter.
4. Before testing, the sample should also ensure that its surface is flat and smooth, free of oxides and other dirt.


